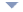
Flower-o-Fire : September 09, 2008

Image Data
File Name: 20D_54426
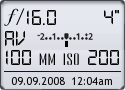
Model: Canon EOS 20D
Lens: Canon EF 100mm F/2.8 USM Macro
Date: 09.09.08 12:04am
Focal Length: 100mm (160mm)
Shutter: 4 s
F-Stop: F16
ISO: 200
Program: Aperture priority
Metering Mode: Evaluative
Flash: Off
Focus Mode: Manual focus
File Name: 20D_54426
Model: Canon EOS 20D
Lens: Canon EF 100mm F/2.8 USM Macro
Date: 09.09.08 12:04am
Focal Length: 100mm (160mm)
Shutter: 4 s
F-Stop: F16
ISO: 200
Program: Aperture priority
Metering Mode: Evaluative
Flash: Off
Focus Mode: Manual focus
Scent is one method flowers use to attract pollinators and some of those scents are pleasant to our sense of smell. Not all flower scents are appealing to humans, though. A number of flowers are pollinated by insects that are attracted to rotten flesh and have flowers that smell like dead animals, often called Carrion flowers, including Rafflesia, the titan arum, and the North American pawpaw. Flowers pollinated by night visitors, including bats and moths, are likely to concentrate on scent to attract pollinators and most such flowers are white.
Flowers commonly have glands called nectaries on various parts that attract animals looking for nutritious nectar. Birds and bees having color vision, enables them to seek out "colorful" flowers. Some flowers have patterns, called nectar guides, that show pollinators where to look for nectar; they may be visible only under ultraviolet light, which is visible to bees and some other insects.
Still other flowers use mimicry to attract pollinators. Some species of orchids, for example, produce flowers resembling female bees in color, shape, and scent. Male bees move from one such flower to another in search of a mate.
Flowers commonly have glands called nectaries on various parts that attract animals looking for nutritious nectar. Birds and bees having color vision, enables them to seek out "colorful" flowers. Some flowers have patterns, called nectar guides, that show pollinators where to look for nectar; they may be visible only under ultraviolet light, which is visible to bees and some other insects.
Still other flowers use mimicry to attract pollinators. Some species of orchids, for example, produce flowers resembling female bees in color, shape, and scent. Male bees move from one such flower to another in search of a mate.











 Subscribe
Subscribe