Arrrrrrch : August 21, 2008
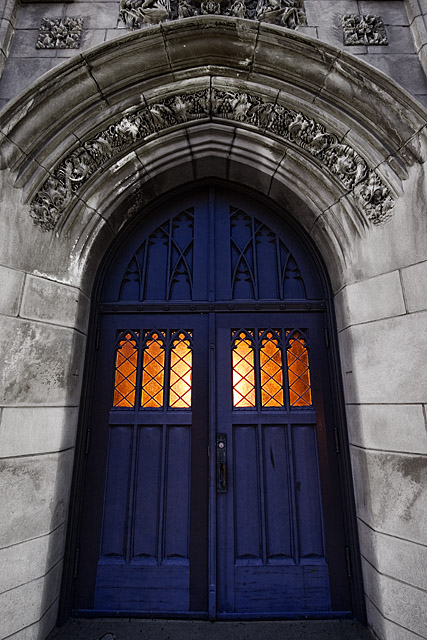

Image Data
File Name: 20D_47469
Model: Canon EOS 20D
Lens: Canon EF-S 10-22mm F/3.5-4.5 USM
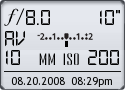
Date: 08.20.08 8:29pm
Focal Length: 10mm (16mm)
Shutter: 10 s
F-Stop: F8
ISO: 200
Program: Aperture priority
Metering Mode: Evaluative
Flash: Off
Focus Mode: Manual focus
File Name: 20D_47469
Model: Canon EOS 20D
Lens: Canon EF-S 10-22mm F/3.5-4.5 USM
Date: 08.20.08 8:29pm
Focal Length: 10mm (16mm)
Shutter: 10 s
F-Stop: F8
ISO: 200
Program: Aperture priority
Metering Mode: Evaluative
Flash: Off
Focus Mode: Manual focus
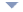
Gothic architecture is a style which flourished during the high and late medieval period. Originating in 12th-century France and lasting into the 16th century, Gothic architecture was known during the period as "the French Style". It evolved from Romanesque architecture and was succeeded by Renaissance architecture.
The defining characteristic of Gothic architecture is the pointed or ogival arch. Arches of this type were used in Islamic architecture before they were used structurally in European architecture, and are thought to have been the inspiration for their use in France.
The Gothic vault, unlike the Roman semi-circular arch, can be used to roof rectangular and irregularly shaped plans such as trapezoids. The other structural advantage is that the pointed arch channels the weight onto the bearing piers or columns at a steep angle. This enabled architects to raise vaults much higher than was possible in Romanesque architecture.
A series of Gothic revivals began in mid-18th century England, spread through 19th-century Europe and continued, largely for ecclesiastical and university structures, into the 20th century.
The defining characteristic of Gothic architecture is the pointed or ogival arch. Arches of this type were used in Islamic architecture before they were used structurally in European architecture, and are thought to have been the inspiration for their use in France.
The Gothic vault, unlike the Roman semi-circular arch, can be used to roof rectangular and irregularly shaped plans such as trapezoids. The other structural advantage is that the pointed arch channels the weight onto the bearing piers or columns at a steep angle. This enabled architects to raise vaults much higher than was possible in Romanesque architecture.
A series of Gothic revivals began in mid-18th century England, spread through 19th-century Europe and continued, largely for ecclesiastical and university structures, into the 20th century.











 Subscribe
Subscribe