Colour Caged : April 02, 2008

Image Data
File Name: 20D_18967
Model: Canon EOS 20D
Lens: Canon EF 100mm F/2.8 USM Macro
Date: 04.01.08 11:32pm
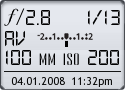
Focal Length: 100mm (160mm)
Shutter: 1/13 s
F-Stop: F2.8
ISO: 200
Program: Aperture priority
Metering Mode: Evaluative
Flash: Off
Focus Mode: Manual focus
File Name: 20D_18967
Model: Canon EOS 20D
Lens: Canon EF 100mm F/2.8 USM Macro
Date: 04.01.08 11:32pm
Focal Length: 100mm (160mm)
Shutter: 1/13 s
F-Stop: F2.8
ISO: 200
Program: Aperture priority
Metering Mode: Evaluative
Flash: Off
Focus Mode: Manual focus
The ability of the human eye to distinguish colors is based upon the varying sensitivity of different cells in the retina to light of different wavelengths. The retina contains three types of color receptor cells, or cones. The first type is most responsive to light that we perceive as violet. The other two types are closely related genetically and chemically, with one most sensitive to light we perceive as yellowish-green and the other most sensitive to green. Light, no matter how complex its composition of wavelengths, is reduced to three color components by the eye.
The other type of light-sensitive cell in the eye, the rod, has a different response curve. In normal situations, when light is bright enough to strongly stimulate the cones, rods play virtually no role in vision at all. On the other hand, in dim light, the cones are understimulated leaving only the signal from the rods, resulting in a colorless response. In certain conditions of intermediate illumination, the rod response and a weak cone response can together result in color discriminations not accounted for by cone responses alone.
The other type of light-sensitive cell in the eye, the rod, has a different response curve. In normal situations, when light is bright enough to strongly stimulate the cones, rods play virtually no role in vision at all. On the other hand, in dim light, the cones are understimulated leaving only the signal from the rods, resulting in a colorless response. In certain conditions of intermediate illumination, the rod response and a weak cone response can together result in color discriminations not accounted for by cone responses alone.
Comments (0)
Colin
04.02.08 12:41pm
"Colour Caged"? When did you turn British?
"Colour Caged"? When did you turn British?










 Subscribe
Subscribe