Copper Sink : May 14, 2008
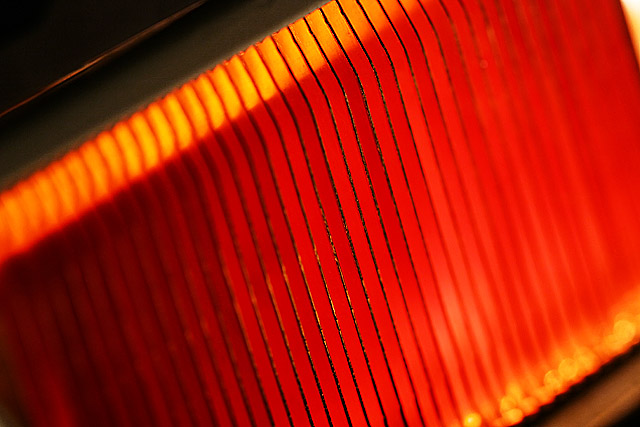
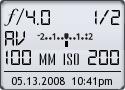
Image Data
File Name: 20D_23330
Model: Canon EOS 20D
Lens: Canon EF 100mm F/2.8 USM Macro
Date: 05.13.08 10:41pm
Focal Length: 100mm (160mm)
Shutter: 1/2 s
F-Stop: F4
ISO: 200
Program: Aperture priority
Metering Mode: Evaluative
Flash: Off
Focus Mode: Manual focus
File Name: 20D_23330
Model: Canon EOS 20D
Lens: Canon EF 100mm F/2.8 USM Macro
Date: 05.13.08 10:41pm
Focal Length: 100mm (160mm)
Shutter: 1/2 s
F-Stop: F4
ISO: 200
Program: Aperture priority
Metering Mode: Evaluative
Flash: Off
Focus Mode: Manual focus
Heat sinks function by efficiently transferring thermal energy from an object at high temperature to a second object at a lower temperature with a much greater heat capacity. This rapid transfer of thermal energy quickly brings the first object into thermal equilibrium with the second, lowering the temperature of the first object, fulfilling the heat sink's role as a cooling device. Efficient function of a heat sink relies on rapid transfer of thermal energy from the first object to the heat sink, and the heat sink to the second object.
The most common design of a heat sink is a metal device with many fins. The high thermal conductivity of the metal combined with its large surface area result in the rapid transfer of thermal energy to the surrounding, cooler, air. This cools the heat sink and whatever it is in direct thermal contact with. A fan may improve the transfer of thermal energy from the heat sink to the air.
Heat sinks are made from a good thermal conductor such as copper or aluminum alloy. Copper is significantly more expensive than aluminum, but is also roughly twice as efficient as a thermal conductor. Aluminum has the significant advantage that it can be easily formed by extrusion, thus making complex cross-sections possible.
The most common design of a heat sink is a metal device with many fins. The high thermal conductivity of the metal combined with its large surface area result in the rapid transfer of thermal energy to the surrounding, cooler, air. This cools the heat sink and whatever it is in direct thermal contact with. A fan may improve the transfer of thermal energy from the heat sink to the air.
Heat sinks are made from a good thermal conductor such as copper or aluminum alloy. Copper is significantly more expensive than aluminum, but is also roughly twice as efficient as a thermal conductor. Aluminum has the significant advantage that it can be easily formed by extrusion, thus making complex cross-sections possible.
Comments (0)
Colin
05.14.08 6:34pm
Don't forget black body radiation. I'm surprised more heat sinks aren't painted black with good heat conducting paint.
Probably because Cu and Al are shiny and pretty!
Don't forget black body radiation. I'm surprised more heat sinks aren't painted black with good heat conducting paint.
Probably because Cu and Al are shiny and pretty!










 Subscribe
Subscribe