Con Fused : April 26, 2008

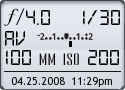
Image Data
File Name: 20D_21151
Model: Canon EOS 20D
Lens: Canon EF 100mm F/2.8 USM Macro
Date: 04.25.08 11:29pm
Focal Length: 100mm (160mm)
Shutter: 1/30 s
F-Stop: F4
ISO: 200
Ex Bias: +1/3
Program: Aperture priority
Metering Mode: Evaluative
Flash: Off
Focus Mode: One shot AF
File Name: 20D_21151
Model: Canon EOS 20D
Lens: Canon EF 100mm F/2.8 USM Macro
Date: 04.25.08 11:29pm
Focal Length: 100mm (160mm)
Shutter: 1/30 s
F-Stop: F4
ISO: 200
Ex Bias: +1/3
Program: Aperture priority
Metering Mode: Evaluative
Flash: Off
Focus Mode: One shot AF
Here we have a collection of automotive blade fuses rated from 5-30 amps. An electrical fuse is a type of overcurrent protection device. Its essential component is a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows, which breaks the circuit in which it is connected, thus protecting the circuit's other components from damage due to excessive current.
A practical fuse was one of the essential features of Thomas Edison's electrical power distribution system. An early fuse was said to have successfully protected an Edison installation from tampering by a rival gas-lighting concern.
Fuses (and other overcurrent devices) are an essential part of a power distribution system to prevent fire or damage. When too much current flows through a wire, it may overheat and be damaged, or even start a fire. Wiring regulations give the maximum rating of a fuse for protection of a particular circuit. Fuses are selected to allow passage of normal currents, but to quickly interrupt a short circuit or overload condition.
A practical fuse was one of the essential features of Thomas Edison's electrical power distribution system. An early fuse was said to have successfully protected an Edison installation from tampering by a rival gas-lighting concern.
Fuses (and other overcurrent devices) are an essential part of a power distribution system to prevent fire or damage. When too much current flows through a wire, it may overheat and be damaged, or even start a fire. Wiring regulations give the maximum rating of a fuse for protection of a particular circuit. Fuses are selected to allow passage of normal currents, but to quickly interrupt a short circuit or overload condition.










 Subscribe
Subscribe